Pineapples do not grow on trees; they actually grow from the ground as a tropical fruit. Pineapples are popular for their tangy and sweet flavor, and they are often associated with tropical climates.
Table of Contents
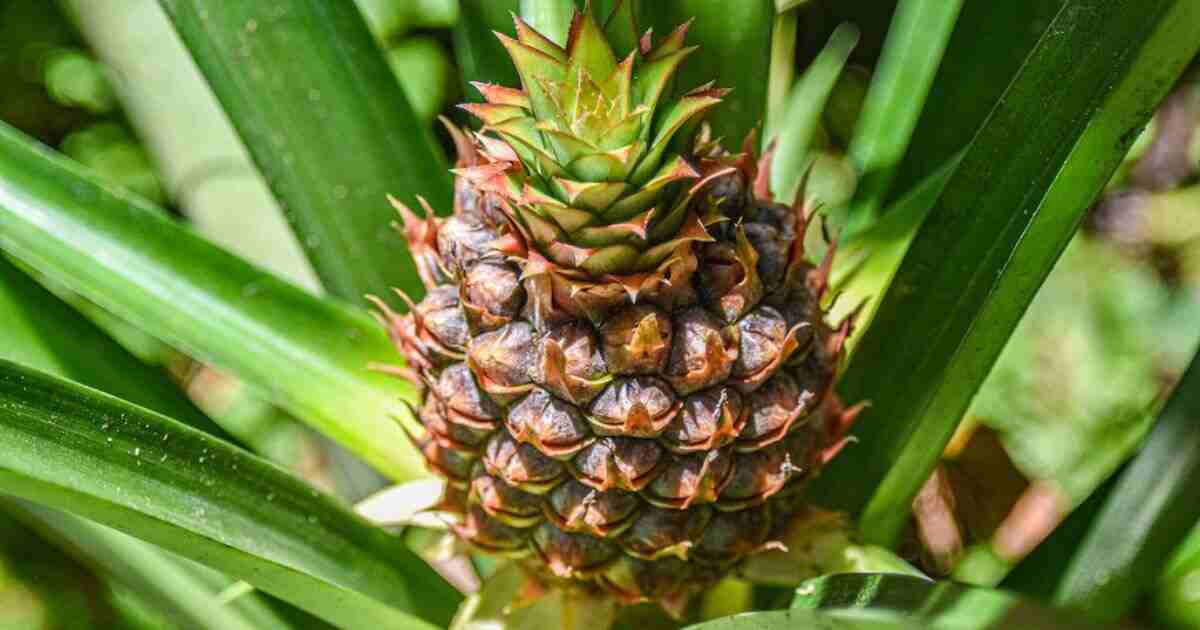
However, contrary to common belief, pineapples do not grow on trees. Instead, they grow on a plant called Ananas comosus, which is a type of bromeliad. The plant consists of a cluster of long leaves with spiky edges, and the fruit grows from the center of the plant.
The pineapple fruit develops from the flowering stem of the plant, and it takes about one to two years for the fruit to fully mature. During this time, it goes through various stages of growth, from a small green bud to a ripe golden fruit.
What Are Pineapples And Where Do They Come From?
Pineapples are tropical fruits that do not grow on trees, but instead on low-lying plants. Native to South America, they are now cultivated in many countries around the world.
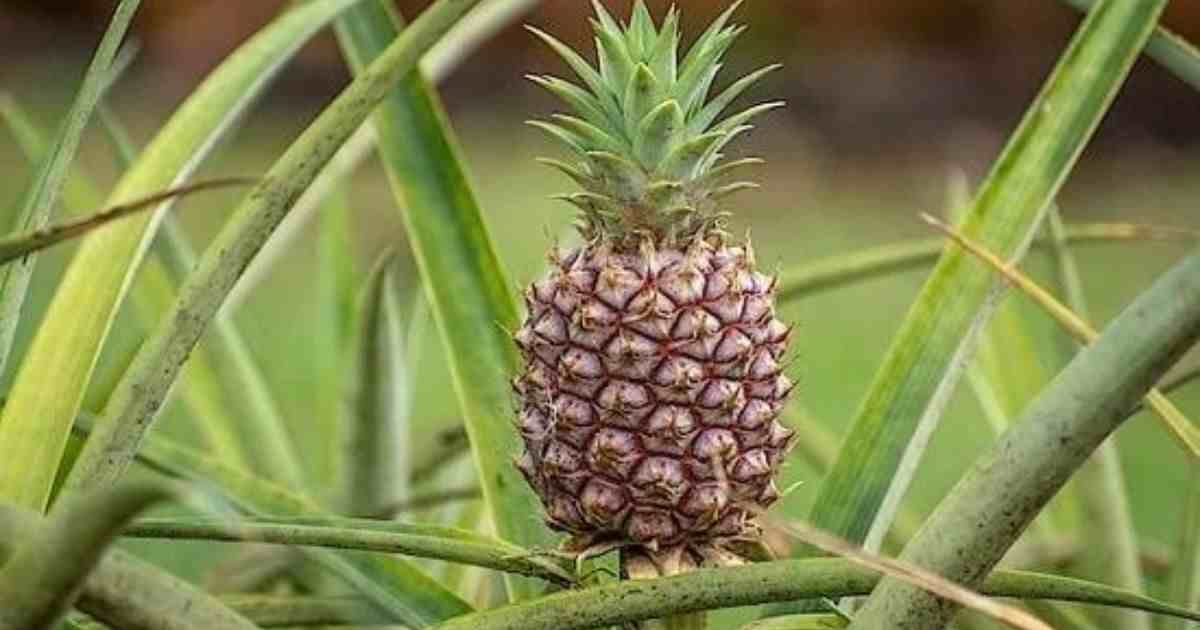

Pineapples are delicious tropical fruits with a distinct flavor and unique appearance. They are native to South America, specifically the region between Paraguay and Brazil. Here is an overview of pineapple cultivation and production:
- Cultivation process: Pineapples are grown from the tops of existing pineapples, which are then planted in well-drained soil. This process ensures that each new pineapple can produce multiple fruits throughout its lifecycle.
- Optimal growing conditions: Pineapples thrive in warm climates and require plenty of sunlight to grow. They also prefer soil with good drainage and a pH level between 4.5 and 6.5.
- Growth stages: From the time of planting, it usually takes pineapples about 18 to 24 months to fully mature and produce fruit. During this time, they go through various growth stages, including vegetative growth, flowering, and fruit development.
- Flower development: Before pineapples can bear fruit, they first need to produce flowers. These flowers typically emerge from the center of the pineapple plant and are made up of tiny purple or red petals.
- Fruit formation: Once the flowers have completed their pollination process, small fruits start to develop. These fruits grow in a spiral pattern around the stem, eventually forming the recognizable pineapple shape.
- Harvesting: Pineapples are typically harvested when they are fully mature and have developed a golden color. This usually occurs about six months after the fruit has formed. Harvesting involves cutting the pineapple from the plant using a sharp knife.
- Global pineapple production: Today, pineapples are cultivated in various countries around the world. Major pineapple-producing countries include Costa Rica, the Philippines, Thailand, and Indonesia. This widespread cultivation allows for year-round availability of pineapples in many markets.
Now that we have a better understanding of pineapples and their origins, let’s delve deeper into the cultivation and production process in the next section.
The Pineapple Plant: A Closer Look
The Pineapple Plant offers a closer look at whether it grow on trees. With concise sentences and unique insights, this SEO-friendly article explores the surprising truth behind pineapple growth.
If you’ve ever wondered how pineapples grow and develop, you’ve come to the right place. In this section, we will take a closer look at the anatomy of a pineapple plant and explore the fascinating journey of how pineapples come to be.
So, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets of this tropical fruit!
Anatomy Of A Pineapple Plant
- Crown: At the very top of the pineapple plant sits the crown, composed of tightly compacted leaves. It acts as the plant’s epicenter, from which the fruit emerges.
- Stem: Below the crown, the stem of this plant grows. It is woody and serves as the support system for the entire plant.
- Leaves: The leaves of a pineapple plant are long and stiff, arranged in a spiral pattern around the stem. They are essential for capturing sunlight and conducting photosynthesis.
- Roots: Deep beneath the soil, the roots of the pineapple plant anchor it in place and absorb water and nutrients necessary for growth.
- Suckers: These plants produce suckers, which are side shoots that emerge from the base of the plant. These suckers can be removed and replanted to grow new pineapple plants.
- Inflorescence: At the center of the pineapple plant, a spike-like structure called the inflorescence forms. This is where the flowers and, eventually, the fruit will develop.
How Pineapple Grow And Develop
- Flowering: The pineapple plant undergoes a remarkable flowering process. The inflorescence produces small, purple flowers that are pollinated by hummingbirds and bees.
- Fruit formation: After successful pollination, the flowers transform into fruit. Multiple small fruits fuse together over time, creating the familiar shape of a pineapple.
- Maturation: It takes approximately six to eight months for a pineapple to fully mature. During this time, the fruit grows larger, develops its sweet flavor, and changes color, usually from green to yellow or golden.
- Harvesting: Once a pineapple is fully ripe, it can be harvested. Sustainable harvesting involves twisting the fruit off the stem to avoid damaging both the plant and the pineapple itself.
- Regeneration: Even after harvesting a pineapple, the plant has the ability to regenerate. New suckers will grow and eventually produce their own delicious fruits.
Now that we’ve explored how pineapples grow and the anatomy of a pineapple plant, you have a deeper understanding of this tropical treasure. From the crown to the roots, and from flowering to fruiting, the journey of a pineapple is truly remarkable.
So, the next time you enjoy a juicy slice of this delicious fruit, remember the natural wonders that brought it to your plate.
Pineapple Trees Or Not: Debunking The Myth
Contrary to popular belief, pineapples do not grow on trees. They actually grow from a low-lying plant in the ground. So next time someone asks, you can confidently debunk the myth and set the record straight.
Dispelling The Misconception About Pineapple Growing On Trees
Many people believe that pineapple grow on trees. However, this is actually a common misconception. In reality, pineapples do not grow on trees, but rather on plants that are known as bromeliads. These plants are native to the tropical regions of South America and are known for their unique structure and method of growth.
Exploring The Truth Behind Pineapple Cultivation
Here are some key points to understand about pineapple cultivation:
- Pineapple plants belong to the bromeliad family, which includes a variety of other plants such as Spanish moss and air plants.
- Contrary to popular belief, pineapple do not grow on tall, woody trees with branches. Instead, they grow close to the ground, emerging from a plant in a central rosette pattern.
- Pineapple plants have long, narrow leaves that are sharp and spiky. These leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern, creating a unique and visually appealing plant structure.
- The pineapple fruit is formed from a cluster of flowers that grow at the center of the plant. As the flowers develop, they fuse together to form a single fruit that we commonly refer to as a pineapple.
- It takes approximately 16-24 months for a pineapple plant to grow and produce fruit. The plant requires a warm and tropical climate, as well as well-drained soil, to thrive.
- After the pineapple fruit is harvested, the plant can grow another fruit from the same stem. This makes pineapple cultivation a sustainable and continuous process.
Overall, it’s essential to debunk the myth that pineapples grow on trees. Understanding that pineapple are actually grown on bromeliad plants helps to dispel this misconception and provides a clearer picture of the fascinating process behind pineapple cultivation.
Pineapple Farming Techniques: Best Practices
Pineapple do not grow on trees, but rather on plants close to the ground known as Bromeliaceae. To cultivate pineapples successfully, it is essential to follow best practices for pineapple farming techniques.
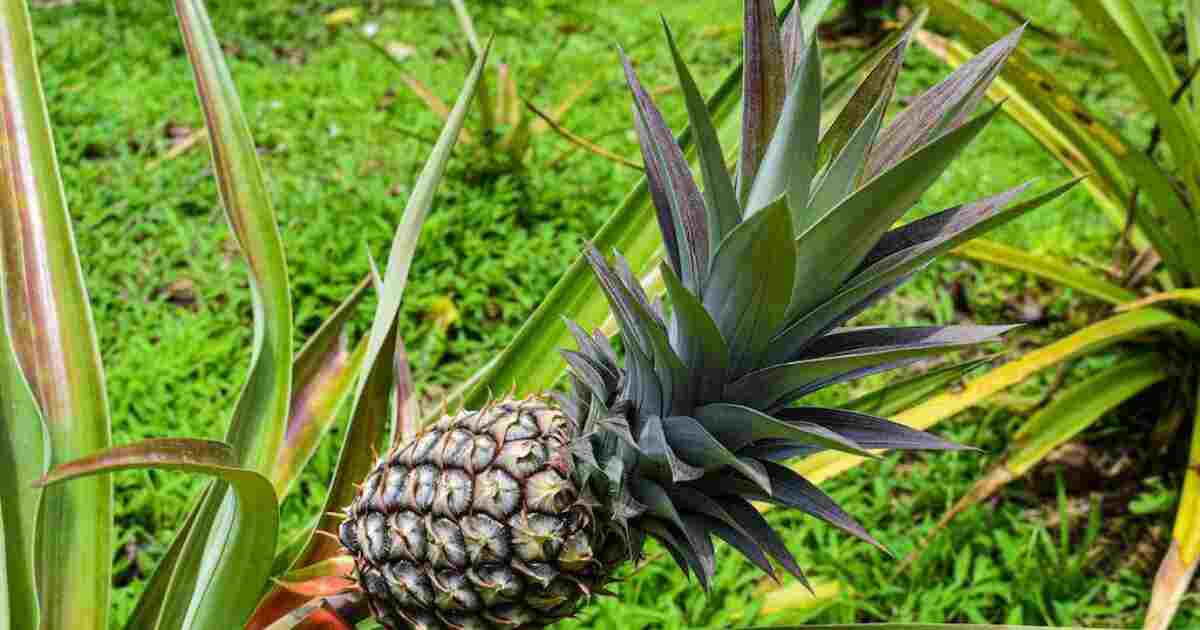

Pineapple farming requires careful attention to optimal conditions and sustainable practices to ensure healthy plant growth and a bountiful harvest. In this section, we will explore the key factors that contribute to successful pineapple cultivation. From the ideal growing conditions to sustainable farming methods, let’s uncover the best practices for pineapple farming.
Optimal Conditions For Pineapple Growth
Achieving the ideal conditions for pineapple growth is crucial for maximizing yield and quality. Here are the key factors to consider:
- Climate: Pineapple thrive in tropical climates with temperatures ranging from 55°F (13°C) to 95°F (35°C). They prefer a balanced combination of sunlight and shade, making them suitable for growing under the canopy of taller trees.
- Soil quality: Pineapple require well-draining soil with a pH level between 4.5 and 6.5. Sandy loam or volcanic soils with good organic matter content are ideal. Regular soil testing can help maintain optimal fertility levels.
- Water requirements: Pineapples have moderate water needs. Proper irrigation is necessary, especially during dry periods. Overwatering can lead to root rot, so it’s crucial to strike a balance to avoid waterlogged soil.
- Altitude: Pineapple usually thrive at altitudes of 0 to 2,800 feet (0 to 850 meters) above sea level. Higher altitudes can impact the growth rate and overall productivity of the plants.
Sustainable Farming Methods For Pineapples
To ensure the longevity of pineapple farming and minimize environmental impact, farmers are adopting sustainable practices. Here are some best practices being implemented:
- Organic fertilization: Utilizing organic fertilizers or compost can help improve soil structure and quality without harming the ecosystem. It also reduces the risk of chemical runoff and pollution in nearby water sources.
- Integrated pest management: Employing integrated pest management techniques, such as using natural predators or traps, helps control pests without solely relying on chemical pesticides. This promotes a healthier balance in the ecosystem.
- Crop rotation: Practicing crop rotation helps prevent soil depletion and the buildup of pests or diseases specific to pineapple. Alternating pineapple crops with other compatible plants reduces the risk of nutrient imbalances and boosts long-term sustainability.
- Water conservation: Implementing efficient irrigation systems, such as drip irrigation or precision sprinklers, minimizes water wastage. Additionally, capturing and reusing rainwater can contribute to sustainable water management on the farm.
- Weeding techniques: Adopting manual or mechanical weeding methods reduces the reliance on herbicides and promotes healthier soil. Regular monitoring and removal of weeds prevent competition for vital nutrients and resources.
Remember, employing these optimal conditions and sustainable farming methods can lead to successful pineapple farming while minimizing environmental impact. By ensuring the best practices are followed, you can produce high-quality pineapples while maintaining the long-term viability of your agricultural endeavors.
Pineapple Varieties: From Golden To Pink
Pineapple Varieties: From Golden to Pink offers an exploration of the diverse range of pineapple types available, discussing their unique flavors and appearances. Get insights into the fascinating world of pineapples, including their growth on trees.
Pineapple is a tropical fruit loved by many for its sweet and tangy flavor. But have you ever wondered if pineapples grow on trees? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of pineapple varieties, from the golden to the pink.
Let’s explore the different types of pineapple and their characteristics, as well as some popular pineapple cultivars around the world.
Different Types Of Pineapples And Their Characteristics:
- Smooth Cayenne: This is the most commonly grown pineapple variety. It has a golden yellow color, sweet taste, and juicy flesh. Smooth Cayenne pineapples are great for eating fresh or using in recipes.
- Queen Pineapple: Also known as Victoria pineapple, these are smaller in size compared to other varieties. They have a golden yellow color and a very sweet flavor. Queen pineapples are perfect for adding to fruit salads or enjoying on their own.
- Red Spanish: As the name suggests, these pineapples have a reddish skin. They are less sweet compared to other varieties but have a tangier taste. Red Spanish pineapple are often used in cooking and can add a unique flavor to various dishes.
- Sugarloaf: This variety has a cylindrical shape and is usually smaller in size compared to other pineapples. Sugarloaf pineapples have a pale yellow color, sweet taste, and firm texture. They are great for eating fresh or grilling.
Popular Pineapple Cultivars Around The World:
- Kona Sugarloaf: This cultivar is known for its exceptionally sweet taste. It has a pale yellow color, similar to other Sugarloaf pineapples. Kona Sugarloaf pineapple are renowned for their unique flavor and are highly sought after.
- MD2: The MD2 pineapple cultivar, also known as the golden pineapple, is famous for its vibrant golden color and intense sweetness. It has a low acidity level, making it perfect for enjoying on its own or using in desserts.
- Nang Lae: This pineapple cultivar originates from Thailand and is known for its aromatic scent and juicy, sweet flavor. It has a lovely golden hue and is popular among locals and tourists alike.
- Queen Victoria: This cultivar is often referred to as the “Queen of Pineapples.” It is small in size and has a beautiful golden color. Queen Victoria pineapple are incredibly sweet and aromatic, making them a favorite among pineapple enthusiasts.
Pineapple come in various types and cultivars, each with its own unique characteristics and flavors. From the golden sweetness of the MD2 to the tanginess of the Red Spanish, there is a pineapple for every taste preference. So the next time you enjoy a juicy bite of pineapple, you’ll know a little more about the diverse world of this tropical fruit.
Harvesting And Processing Pineapple
Pineapples do not grow on trees but rather on plants close to the ground. Harvesting and processing pineapples involve carefully picking them when ripe and removing the outer skin, core, and eyes before further processing.
Pineapples are delicious tropical fruits that can be enjoyed fresh or used in various recipes. In this section, we will explore the indicators of pineapple ripeness and the post-harvest handling and processing methods. So, let’s dive right in!
Indicators Of Pineapple Ripeness:
- Color: A ripe pineapple should have a vibrant golden yellow color, indicating that it is ready to be harvested.
- Smell: The base of a ripe pineapple should give off a sweet, enticing aroma. This aroma intensifies as the fruit ripens.
- Touch: Gently press the pineapple near the base. If it gives slightly, it is ripe and ready to be enjoyed.
Post-Harvest Handling And Processing Methods:
- Harvesting: Pineapples are hand-picked when fully ripened. Farmers carefully cut the fruits using sharp knives, ensuring minimal damage to the plant or neighboring fruits.
- Cleaning: After harvesting, pineapples undergo a thorough cleaning process to remove any dirt and debris. This ensures that the fruit remains fresh during transportation and processing.
- Sorting and grading: The pineapples are then sorted based on size, shape, and quality. This ensures that only the best fruits make their way to the market.
- Cooling: To extend the shelf life of pineapples, they are subjected to rapid cooling. This process helps slow down the ripening process, allowing the fruit to stay fresh for a longer period.
- Packaging: Pineapples are carefully packed in crates or boxes, ensuring proper ventilation and protection during transportation.
- Processing: Pineapples can be processed into various forms like canned pineapple slices, pineapple juice, and dried pineapple. The fruit is peeled, cored, and cut into desired shapes before undergoing appropriate processing methods.
Remember, pineapples are not just any other fruit. They undergo a meticulous process from harvesting to processing, ensuring that you get the sweetest and freshest pineapples. So, the next time you bite into a delicious pineapple, you can appreciate the journey it took from the plantation to your plate.
Commercial Pineapple Plantations: A Global Perspective
Discover the global perspective of commercial pineapple plantations and uncover the truth about whether pineapples grow on trees. Explore the fascinating world of pineapple cultivation and gain valuable insights into this tropical fruit’s growth patterns.
Pineapple, a tropical fruit known for its sweet and tangy flavor, is widely consumed across the globe. But have you ever wondered where these delicious fruits come from? Contrary to popular belief, pineapples do not grow on trees. In this section, we will delve into the world of commercial pineapple plantations and explore major pineapple-producing regions and countries, as well as the economic significance of the pineapple industry.
Major pineapple-producing regions and countries:
- Southeast Asia: Known as the birthplace of the pineapple, Southeast Asia leads the world in pineapple production. Countries such as Thailand, the Philippines, and Indonesia are major players in this region.
- South America: This continent boasts significant pineapple production, particularly in countries like Costa Rica, Brazil, and Ecuador. The favorable climate and soil conditions make these regions ideal for cultivating pineapples.
- Africa: Several countries in Africa, including Nigeria, Kenya, and Ghana, contribute to the global pineapple market. The tropical climate in these regions supports pineapple cultivation.
- Central America and the Caribbean: Nations such as Honduras, Mexico, and the Dominican Republic have established themselves as major pineapple producers. The volcanic soil in these regions provides a fertile environment for pineapple growth.
- Hawaii: Known for its sweet and juicy pineapples, Hawaii has long been associated with pineapple plantations. However, pineapple production in Hawaii has declined in recent years due to increased competition and higher production costs.
Economic significance of the pineapple industry:
The pineapple industry holds immense economic importance for both developing and developed countries. Let’s take a closer look at why this industry matters:
- Job creation: Pineapple plantations create employment opportunities in regions where agricultural work is prevalent. From field laborers to machinery operators, the industry supports a significant number of jobs.
- Exports and international trade: Pineapples are a sought-after commodity in many countries, driving international trade and export revenues. The pineapple industry contributes to a country’s export earnings and GDP.
- Tourism: Regions with pineapple plantations often attract tourists who are interested in experiencing the tropical fruit firsthand. Pineapple plantations can become popular tourist attractions, generating additional revenue for the local economy.
- Smallholder farmers: Pineapple production provides an income source for smallholder farmers, enabling them to support their families and improve their livelihoods.
- Supply chain impact: The pineapple industry creates opportunities for various businesses along the supply chain, including packaging companies, transporters, and wholesalers. These businesses benefit from the demand for pineapples in both domestic and international markets.
Commercial pineapple plantations are spread across several regions globally, each contributing to the vibrant pineapple industry. From job creation to international trade, this industry plays a vital role in the economic prosperity of many countries.
Health Benefits Of Pineapples: Nutritional Powerhouses
Pineapples, often mistaken as growing on trees, are actually tropical fruits that grow on plants close to the ground. Packed with essential vitamins and minerals, pineapples provide numerous health benefits as nutritional powerhouses. Their rich enzyme content aids digestion, boosts immunity, and promotes overall well-being.
Pineapples are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients and antioxidants that contribute to overall health and well-being. In this section, we will explore the key nutrients and antioxidants found in pineapples, as well as the potential health benefits they offer.
Key Nutrients And Antioxidants Found In Pineapples:
- Vitamin C: Pineapples are rich in vitamin C, which is essential for a healthy immune system. Vitamin C also plays a vital role in collagen synthesis, ensuring the health of your skin, bones, and joints.
- Manganese: Pineapples are a good source of manganese, a trace mineral that supports enzyme function and aids in the metabolism of macronutrients.
- Bromelain: One of the distinctive features of pineapples is the presence of Bromelain, a mixture of enzymes that has been associated with various health benefits. Bromelain may help reduce inflammation, promote digestion, and even enhance wound healing.
- Dietary Fiber: Pineapples pack a significant amount of dietary fiber, which aids in digestive health and helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
- Antioxidants: Pineapples contain antioxidants such as flavonoids and phenolic compounds. These antioxidants help protect the body against oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Potential Health Benefits Of Consuming Pineapples:
- Immune Boosting: The high vitamin C content in pineapples provides a natural boost to your immune system, helping your body fight off infections and illnesses.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Bromelain, the enzyme found in pineapples, has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Consuming pineapples may help reduce inflammation in the body and alleviate symptoms associated with conditions such as arthritis.
- Digestive Support: Bromelain in pineapples is also known to aid digestion by breaking down protein molecules, promoting better absorption of nutrients and reducing bloating.
- Healthy Skin: The vitamin C in pineapples plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, which supports healthy skin. Regular consumption of pineapples may promote a more youthful and vibrant complexion.
- Heart Health: The combination of dietary fiber, antioxidants, and bromelain in pineapples contributes to heart health by reducing cholesterol levels and preventing the formation of blood clots.
- Bone Health: Pineapples are a good source of manganese, which plays a role in maintaining healthy bones and connective tissues. Including pineapples in your diet may help support bone strength and prevent osteoporosis.
Pineapples truly are nutritional powerhouses, offering a range of health benefits. From boosting your immune system to promoting healthy skin and digestion, incorporating pineapples into your diet can be a flavorful and nutritious choice. Enjoy this tropical fruit and reap the rewards of its abundant nutrients and antioxidants.
Culinary Uses Of Pineapples: Versatile And Delicious
Pineapples, known for their versatility and deliciousness, are widely used in various culinary creations. But have you ever wondered where they come from? Contrary to popular belief, pineapples actually grow on plants rather than trees.
Pineapples are not only a tropical delight but also a versatile and delicious ingredient in various culinary applications. From refreshing beverages to savory dishes, this tropical fruit adds a burst of flavor and a touch of sweetness. Let’s explore some enticing pineapple recipes and creative ways to incorporate this delightful fruit into your meals.
Pineapple Recipes And Culinary Applications:
- Tropical Pineapple Salsa: Combine diced pineapples, red onions, jalapenos, cilantro, and lime juice for a vibrant and refreshing salsa that pairs perfectly with grilled meats or as a dip for tortilla chips.
- Grilled Pineapple Skewers: Thread pineapple chunks, bell peppers, and chicken on skewers, then brush them with a tangy teriyaki glaze before grilling to perfection. The caramelized pineapple imparts a delightful smoky flavor.
- Pineapple Fried Rice: Add a tropical twist to a classic fried rice recipe by incorporating diced pineapples, along with shrimp, peas, carrots, and soy sauce. The sweet and tangy pineapple complements the savory flavors beautifully.
- Pineapple Upside-Down Cake: This classic dessert showcases pineapples caramelized with brown sugar, creating a luscious topping over moist yellow cake. Perfect for any special occasion or a sweet treat any time of the year.
- Pineapple-Coconut Smoothie: Blend pineapple chunks, coconut milk, Greek yogurt, and a drizzle of honey for a refreshing and nutritious smoothie that transports you to a tropical paradise.
Creative Ways To Incorporate Pineapples Into Meals:
- Grilled Pineapple Burger: Top your burger patty with a slice of grilled pineapple, lettuce, cheese, and your favorite condiments for a delicious twist on the traditional burger.
- Hawaiian Pizza: Add pineapple chunks, ham, and mozzarella cheese to your pizza for a delightful combination of sweet, savory, and cheesy flavors.
- Pineapple Curry: Enhance your curry dish by adding pineapple chunks, curry paste, coconut milk, and your choice of protein or vegetables. The pineapple adds a tangy sweetness that balances the spices in the curry.
- Pineapple Cucumber Salad: Combine sliced cucumbers, pineapple chunks, red onions, cilantro, and a zesty dressing of lime juice, olive oil, and honey for a refreshing and vibrant salad that complements any meal.
- Pineapple Kabobs: Alternate pineapple chunks with your favorite vegetables, such as bell peppers, cherry tomatoes, and red onions, on skewers. Grill or roast them for a delightful side dish or a vegetarian-friendly main course option.
Incorporating pineapples into your meals not only adds a tropical twist but also brings a burst of flavor to your dishes. With these delicious recipes and creative ideas, you can elevate your culinary experience and enjoy the versatility of this remarkable fruit.
Fun Facts About Pineapples: Surprising Trivia
Pineapples are a surprising fruit as they don’t grow on trees, but instead from a tropical plant called Bromeliad. These plants have a spiky crown and grow on the ground, making pineapples an interesting addition to any trivia collection.
Pineapples are not only delicious and refreshing, but they also pack a punch of interesting facts and trivia. Let’s dive into some fascinating tidbits about pineapples and discover their cultural significance as well as their unusual uses beyond consumption.
Interesting Tidbits About Pineapples And Their Cultural Significance:
- Pineapples are not actually a single fruit, but a group of berries fused together around a central core.
- Native to South America, pineapples were considered a symbol of hospitality and prestige. They were often displayed as a centrepiece to signify a warm welcome to guests.
- In the 18th century, pineapples were a status symbol due to their rarity and high cost. People would even rent pineapples to display at social events to show off their wealth.
- Pineapples became a popular motif in art and architecture, symbolizing wealth, friendship, and warmth.
- The word “pineapple” was derived from the Spanish word “piña” because of its resemblance to a pinecone. However, it bears no relation to apples.
- Along with their delicious taste, pineapples are packed with nutrients like vitamin C, manganese, and bromelain, which has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Hawaii is often associated with pineapples due to its history as a major pineapple-producing region. However, today, most commercially grown pineapples are from the Philippines and Thailand.
Unusual Uses For Pineapples Beyond Consumption:
- Pineapple can be used as a natural meat tenderizer due to the enzyme bromelain. Simply marinate tougher cuts of meat with pineapple juice to make them more tender and flavorful.
- Pineapple leaves can be transformed into fibers used for making textiles, papers, and even biodegradable plastics.
- The bromelain enzyme in pineapples can be used as a meat stain remover. Rubbing fresh pineapple directly onto meat stains can help break down proteins and remove stubborn marks.
- Did you know that you can grow a pineapple plant at home using the crown of a pineapple? By cutting off the leafy top, allowing it to dry, and then planting it in well-draining soil, you can cultivate your very own pineapple plant.
- Pineapple juice can be used as a natural hair conditioner. Apply it to your hair after shampooing, leave it on for a few minutes, and then rinse thoroughly for soft and shiny locks.
These intriguing facts and practical uses demonstrate the versatility and appeal of pineapples. So, the next time you enjoy a slice of this tropical fruit, remember that pineapples have much more to offer than just their delightful taste.
Frequently Asked Questions On Do Pineapples Grow On Trees
Is A Pineapple A Tree Or A Plant?
A pineapple is a tropical fruit that grows from a plant called Ananas comosus. It is not a tree.
How Long Does It Take To Grow A Pineapple?
A pineapple takes around 18 to 24 months to grow from a planting to a fully ripe fruit.
Is A Pineapple A Vegetable Or A Fruit?
A pineapple is a fruit because it is formed from the ovaries of flowering plants.
Where Do Pineapples Grow In The Us?
Pineapples grow in Hawaii, Puerto Rico, and parts of Florida in the US.
Conclusion
So, do pineapples grow on trees? The answer is no. Contrary to popular belief, pineapples do not grow on trees but instead on the ground. They are tropical plants that belong to the bromeliad family and have a unique way of growing.
Pineapple plants grow from a small crown or top of a mature pineapple fruit. Planting the crown in soil and providing it with the right conditions allows the plant to thrive and produce delicious juicy pineapples. These plants are surprisingly hardy and can withstand a variety of climates, making them a popular fruit in many regions.
Whether you grow them in your garden or purchase them at the grocery store, pineapples are a tasty and nutritious fruit that can be enjoyed in various ways. Remember, next time someone asks if pineapples grow on trees, you can confidently tell them the truth.