Vitamin c is the only water-soluble vitamin among the given options. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water and are not stored in the body.
The excess amount of these vitamins is excreted through urine. Since they are not stored in the body, they need to be consumed daily through a balanced diet to maintain good health. Vitamin c, also known as ascorbic acid, is a crucial nutrient for various bodily functions, including the development and maintenance of tissues, protection against free radical damage, and aiding the absorption of iron.
It is found in citrus fruits, strawberries, tomatoes, broccoli, and other green leafy vegetables. Other water-soluble vitamins include the b-vitamins (b1, b2, b3, b5, b6, b7, b9, and b12). A deficiency in any of these vitamins can lead to various health problems such as anemia, nerve damage, and birth defects in infants.

Credit: www.medicalnewstoday.com
Benefits Of Water-Soluble Vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins are a crucial part of our daily diet, as they are not stored in the body, and require constant replenishment. These vitamins are easily dissolved in water and absorbed in the bloodstream, which helps maintain regular bodily functions.
Here are some essential benefits of consuming these vitamins in proper amounts:
Definition Of Water-Soluble Vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins are essential nutrients that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be regularly obtained through our diet. These include vitamin b complex (b1, b2, b3, b5, b6, b7, b9, b12) and vitamin c. these vitamins are called water-soluble because they dissolve in water and are not stored in large amounts in the body.
Importance Of Consuming Them In Proper Amounts
Water-soluble vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining our bodily functions and overall health. They are essential for proper metabolism, growth, development, and overall body health. The main advantages of consuming these vitamins are that they help in:
- Boosting the immune system
- Preventing chronic diseases
- Enhancing iron absorption
- Promoting healthy skin, hair, and nails
- Combating fatigue and depression
How Water-Soluble Vitamins Benefit The Body
Water-soluble vitamins perform several critical functions in the body. Here are some benefits:
- Vitamin b: Helps in maintaining healthy skin, muscles, and bones, and aids in the formation of red blood cells.
- Vitamin c: Helps boost the immune system by shielding the body against viruses and infections. It also aids in collagen formation and improves absorption of iron from plant sources.
- B-complex vitamins: Promote energy production, aid in maintaining a healthy nervous system and benefit the heart, skin, and eyes.
It is important to remember that consuming water-soluble vitamins in excess can lead to toxicity, so it is crucial to stick to the recommended daily intake. Consuming a diet rich in water-soluble vitamins is vital for maintaining overall health and keeping diseases at bay.
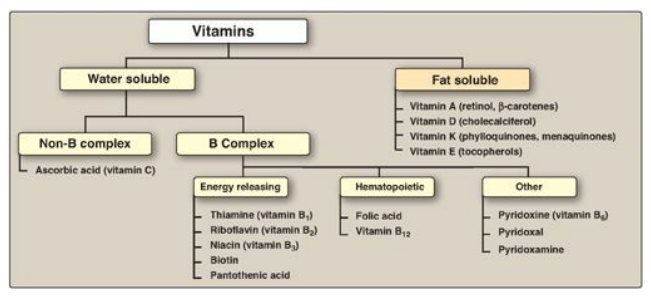
Types Of Water-Soluble Vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins are a type of nutrient that is essential for our overall health and well-being. Unlike fat-soluble vitamins that are stored in our body over long periods, water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water and are not stored within the body.
In this blog post, we will be focusing on the types of water-soluble vitamins and their benefits. ###
Explanation of each type of vitamin and their benefits:
Vitamin b-complex:
Vitamin b-complex includes a group of eight water-soluble vitamins that play a crucial role in our energy production, brain function, and cell metabolism. The eight b vitamins include thiamin (b1), riboflavin (b2), niacin (b3), pantothenic acid (b5), pyridoxine (b6), biotin (b7), folate (b9), and cobalamin (b12).
Functions and health benefits of each b vitamin:
● thiamin (b1) helps convert food into energy, supports our immune function, and plays a role in nerve function.
● riboflavin (b2) contributes to the production of red blood cells and maintains healthy skin.
● niacin (b3) helps improve cholesterol levels and supports healthy brain function.
● pantothenic acid (b5) is involved in the production of hormones and cholesterol and supports wound healing.
● pyridoxine (b6) helps produce serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, and produces red blood cells.
● biotin (b7) supports healthy hair, skin, and nails.
● folate (b9) is essential for proper brain function and tissue growth and development.
● cobalamin (b12) helps produce dna and red blood cells and maintains a healthy nervous system.
Food sources for each vitamin:
Sources of vitamin b-complex include:
● whole grains, meats, and legumes for thiamin and riboflavin.
● meats, fish, and poultry for niacin and pyridoxine.
● avocado, broccoli, and sweet potato for pantothenic acid.
● eggs, dairy products, and nuts for biotin.
● dark leafy greens, asparagus, and beans for folate.
● meats, fish, and dairy products for cobalamin.
Recommended daily intake:
The recommended daily intake of vitamin b-complex varies depending on age, sex, and specific health conditions. However, an average adult’s recommended daily intake of vitamin b-complex is as follows:
● thiamin (b1): 1. 2 mg/day for men and 1. 1 mg/day for women
● riboflavin (b2): 1. 3 mg/day for men and 1. 1 mg/day for women
● niacin (b3): 16 mg/day for men and 14 mg/day for women
● Pantothenic Acid (B5): 5 Mg/Day
● pyridoxine (b6): 1. 7 mg/day for men and 1. 5 mg/day for women
● Biotin (B7): 30 Mcg/Day
● Folate (B9): 400 Mcg/Day For Adults
● Cobalamin (B12): 2.4 Mcg/Day
Vitamin c:
Vitamin c, also known as ascorbic acid, is an essential water-soluble vitamin that plays a critical role in our immune function, wound healing, and the production of collagen.
Functions and health benefits:
● helps to boost the immune system by promoting the production of white blood cells.
● acts as a powerful antioxidant, helping to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
● promotes the production of collagen to support healthy skin and wound healing.
● helps to enhance iron absorption.
Food sources for vitamin c:
Sources of vitamin c include:
● citrus fruits, such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruit.
● berries, such as strawberries, raspberries, and blueberries.
● melons, such as watermelon and cantaloupe.
● vegetables, such as broccoli, tomatoes, and bell peppers.
Recommended daily intake:
The recommended daily intake of vitamin c varies depending on age, sex, and specific health conditions. However, an average adult’s recommended daily intake of vitamin c is 90 mg for men and 75 mg for women.
Water-soluble vitamins are essential for our overall health and should be consumed daily through a balanced diet. Incorporating vitamin b-complex and vitamin c rich foods in our diet can help us maintain a healthy immune system and promote healthy skin and cell function.
How To Determine Which Water-Soluble Vitamin You Need
Which of the following vitamins is water soluble – how to determine which water-soluble vitamin you need
Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water and are not stored in the body. This means that they need to be consumed daily to prevent deficiency and maintain general health. There are nine water-soluble vitamins: eight b vitamins and vitamin c. here’s how to determine which water-soluble vitamin you need.

Factors To Consider Before Choosing A Supplement
Before choosing a vitamin supplement, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Age: Different age groups require different amounts of water-soluble vitamins.
- Gender: Men and women have different nutritional needs.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding need more water-soluble vitamins.
- Lifestyle: Athletes, smokers, and people who drink alcohol may need more vitamins.
- Health conditions: Certain health conditions may require additional water-soluble vitamins.
Genetics And Individual Variation
Individuals may have different genetic variations that affect their vitamin requirements. For example, some people may have a genetic variation that affects their ability to absorb or metabolize certain vitamins. Genetic testing can help identify these variations and provide personalized recommendations for vitamin intake.
Dietary Restrictions And Health Conditions
People with dietary restrictions or certain health conditions may need to take a water-soluble vitamin supplement to prevent deficiency. For example, vegetarians and vegans may need to take a vitamin b12 supplement, as this vitamin is predominantly found in animal-derived foods.
People with malabsorption and digestive disorders may also need to take a supplement to prevent deficiency.
Best Way To Get Water-Soluble Vitamins From Food
While taking a supplement can help prevent deficiency, the best way to get water-soluble vitamins is through a healthy and balanced diet. Here are some great dietary sources of water-soluble vitamins:
- Vitamin b1: Sunflower seeds, pork, whole grains.
- Vitamin b2: Dairy products, green leafy vegetables, almonds.
- Vitamin b3: Chicken, salmon, peanuts.
- Vitamin b5: Avocados, mushrooms, sweet potatoes.
- Vitamin b6: Bananas, poultry, fish.
- Vitamin b7: Eggs, almonds, sweet potatoes.
- Vitamin b9: Leafy greens, legumes, citrus fruits.
- Vitamin b12: Beef, fish, dairy products.
- Vitamin c: Citrus fruits, broccoli, strawberries.
Getting enough water-soluble vitamins is essential for maintaining good health. By considering your individual factors and choosing the best dietary sources, you can easily get enough of these essential vitamins.

Risks And Side Effects Of Water-Soluble Vitamins
Which of the following vitamins is water soluble: risks and side effects of water-soluble vitamins
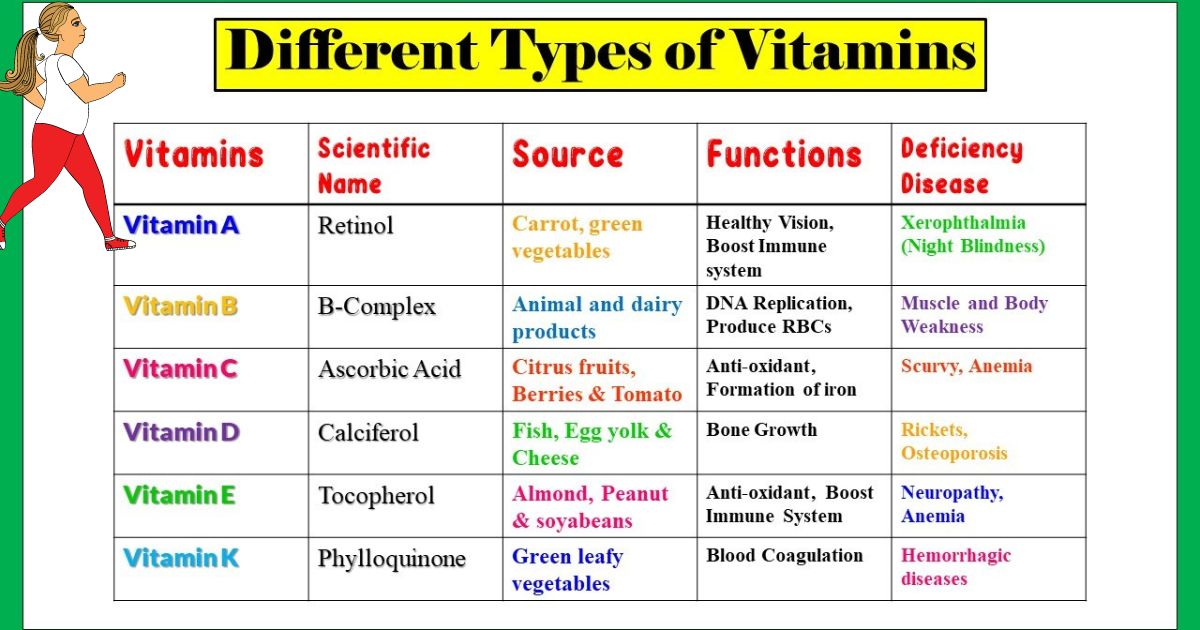
Vitamins are necessary for maintaining a healthy body, mind, and spirit. But do you know which of the following vitamins are water-soluble? They are vitamins b1, b2, b3, b5, b6, b7, b9, b12, and vitamin c.
While water-soluble vitamins are essential for the human body, overconsumption can lead to health issues. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the potential risks and side effects of consuming too much of certain vitamins.
Overview Of Potential Risks And Side Effects Of Consuming Too Much Of Certain Vitamins
Overconsumption of water-soluble vitamins can cause several health problems. Some of the potential risks and side effects include:
- Kidney damage
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Stomach cramps
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Skin rashes
Impact Of Overconsumption On The Body
Overconsumption of vitamins can affect different parts of your body. The impact includes:
- Vitamin b3 (niacin) – overdose of vitamin b3 can lead to flushing, itching, and liver damage.
- Vitamin b6 (pyridoxine) – excess vitamin b6 can damage your nerves that can cause numbness and tingling sensations in the extremities, which can become irreversible over time.
- Vitamin c (ascorbic acid) – high amounts of vitamin c can lead to nausea, diarrhea, and stomach cramps.
Safe Upper Limits For Each Vitamin
Knowing the recommended safe upper limits for each vitamin is essential to avoid potential vitamin toxicity. Here are the safe upper limits for each water-soluble vitamin:
- Vitamin b1 (thiamin) – no established upper limit
- Vitamin b2 (riboflavin) – no established upper limit
- Vitamin b3 (niacin) – 35 milligrams/day
- Vitamin b5 (pantothenic acid) – no established upper limit
- Vitamin b6 (pyridoxine) – 100 milligrams/day
- Vitamin b7 (biotin) – no established upper limit
- Vitamin b9 (folate) – 1,000 micrograms/day
- Vitamin b12 (cobalamin) – no established upper limit
- Vitamin c (ascorbic acid) – 2,000 milligrams/day
Water-soluble vitamins are essential for your health but can cause health issues when consumed excessively. Knowing the risks and imited safe upper limits will help you maintain a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions On Which Of The Following Vitamins Is Water Soluble
Which Vitamins Are Water Soluble And What Does This Mean?
Water-soluble vitamins are vitamins that dissolve in water and cannot be stored by the body. They include vitamins b1, b2, b3, b5, b6, b7, b9, b12, and vitamin c.
Why Are Water-Soluble Vitamins Important?
Water-soluble vitamins are important for maintaining good health and preventing diseases. They are needed for many vital processes in the body, including metabolism, the immune system, and the nervous system.
What Happens When You Have Too Much Water-Soluble Vitamins?
Having too much of water-soluble vitamins can lead to vitamin toxicity, which can cause serious health problems. However, because these vitamins are excreted in urine, it is harder to consume toxic levels of water-soluble vitamins than fat-soluble vitamins.
How Can I Get Enough Water-Soluble Vitamins In My Diet?
You can get water-soluble vitamins from a healthy diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Vitamin supplements can also help, but it is best to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
What Happens If I Don’T Get Enough Water-Soluble Vitamins?
A deficiency in water-soluble vitamins can cause serious health problems. Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, anemia, and nerve damage. It is important to ensure that you are getting enough water-soluble vitamins in your diet or through supplements.
Conclusion
Given the range of health benefits that come from consuming vitamins, it is important to understand which types are water-soluble. B vitamins (including b1, b2, b3, b5, b6, b7, b9, and b12) and vitamin c are the main water-soluble vitamins.
However, it’s important to be mindful that consuming excessive amounts of these vitamins can lead to negative side effects. Keeping a balanced diet with a variety of fruits, vegetables, and grains will ensure that your body is receiving adequate amounts of essential vitamins.
As opposed to fat-soluble vitamins, which can accumulate in our bodies and cause harm, water-soluble vitamins are excreted in urine. This means that it is important to consume these vitamins regularly in order to receive the maximum health benefits. Understanding the difference between water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins can help you make more informed decisions about your own personal health and nutrition.




